Anestacon Jelly
Generic name:lidocaine hydrochloride
Dosage form: jelly
Drug class:Topical anesthetics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 22, 2021.
On This Page
Rx Only
Anestacon Jelly Description
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Jelly USP, 2% (Anestacon®) is a sterile aqueous product that contains a local anesthetic agent and is administered topically. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE for specific uses.)
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Jelly USP, 2% (Anestacon®) contains lidocaine HCl which is chemically designated as acetamide, 2- (diethyl-amino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride and has the following structural formula:
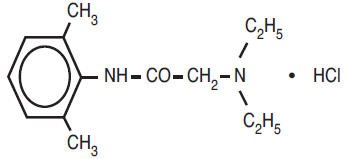
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Jelly USP, 2% (Anestacon®) also contains hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and the resulting mixture maximizes contact with mucosa and provides lubrication for instrumentation. The unused portion should be discarded after initial use.
Composition of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Jelly USP, 2% (Anestacon®) 15 mL bottle: Each mL contains 20 mg of lidocaine HCl. The formulation also contains benzalkonium chloride, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, purified water, sodium chloride, and sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid to adjust pH to 6.0–7.0.
Anestacon Jelly - Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Lidocaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action.
Onset of Action
The onset of action is 3–5 minutes. It is ineffective when applied to intact skin.
Hemodynamics
Excessive blood levels may cause changes in cardiac output, total peripheral resistance, and mean arterial pressure. These changes may be attributable to a direct depressant effect of the local anesthetic agent on various components of the cardiovascular system.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes, its rate and extent of absorption depending upon concentration and total dose administered, the specific site of application, and duration of exposure. In general, the...



