Protopam
Generic name:pralidoxime chloride
Dosage form: injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Drug class:Antidotes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 22, 2021.
On This Page
Protopam Description
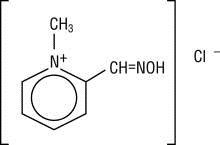
Chemical name: 2-formyl-1-methylpyridinium chloride oxime. Available in the United States as Protopam Chloride for Injection (Protopam Chloride), pralidoxime chloride is frequently referred to as 2-PAM Chloride.
Structural formula:
Pralidoxime chloride occurs as an odorless, white, nonhygroscopic, crystalline powder which is soluble in water. Stable in air, it melts between 215º and 225º C, with decomposition.
The specific activity of the drug resides in the 2-formyl-1-methylpyridinium ion and is independent of the particular salt employed. The chloride is preferred because of physiologic compatibility, excellent water solubility at all temperatures, and high potency per gram, due to its low molecular weight.
Pralidoxime chloride is a cholinesterase reactivator.
Protopam Chloride for intravenous injection or infusion is prepared by cryo-desiccation. Each vial contains 1000 mg of sterile pralidoxime chloride, and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, to be reconstituted with 20 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP. The pH of the reconstituted solution is 3.5 to 4.5. Intramuscular or subcutaneous injection may be used when intravenous injection is not feasible.
Protopam - Clinical Pharmacology
The principal action of pralidoxime chloride is to reactivate cholinesterase (mainly outside of the central nervous system) which has been inactivated by phosphorylation due to an organophosphate pesticide or related compound. The destruction of accumulated acetylcholine can then proceed, and neuromuscular junctions will again function normally. Pralidoxime chloride also slows the process of “aging” of phosphorylated cholinesterase to a nonreactivatable form, and detoxifies certain organophosphates by direct chemical reaction. The drug has its most critical effect in relieving paralysis of the mus...