Vetprofen
Generic name: carprofen tablets
Dosage form: FOR ANIMAL USE ONLY
On This Page
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
For oral use in dogs only
CAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Vetprofen Description
Vetprofen (carprofen) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the propionic acid class that includes ibuprofen, naproxen, and ketoprofen. Carprofen is the nonproprietary designation for a substituted carbazole, 6-chloro-α-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-acetic acid. The empirical formula is C15H12ClNO2 and the molecular weight 273.72. The chemical structure of carprofen is:
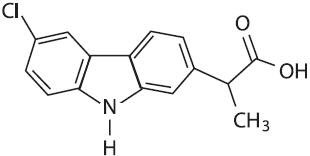
Carprofen is a white, crystalline compound. It is freely soluble in ethanol, but practically insoluble in water at 25°C.
Vetprofen - Clinical Pharmacology
Carprofen is a non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with characteristic analgesic and antipyretic activity approximately equipotent to indomethacin in animal models.1
The mechanism of action of carprofen, like that of other NSAIDs, is believed to be associated with the inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity. Two unique cyclooxygenases have been described in mammals.2 The constitutive cyclooxygenase, COX-1, synthesizes prostaglandins necessary for normal gastrointestinal and renal function. The inducible cyclooxygenase, COX-2, generates prostaglandins involved in inflammation. Inhibition of COX-1 is thought to be associated with gastrointestinal and renal toxicity while inhibition of COX-2 provides anti-inflammatory activity. The specificity of a particular NSAID for COX-2 versus COX-1 may vary from species to species.3 In an in vitro study using canine cell cultures, carprofen demonstrated selective inhibition of COX-2 versus COX-1.4 Clinical relevance of these data has not been shown. Carprofen has also been shown to inhibit the release of several prostaglandins in two inflammatory cell systems: rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and human rheumatoid synovial cells, indicating inhibition of acute (PMN system) and chronic (synovial cell system) inflammatory reactions.1
Several studies have demonstrated that carprofen has modulatory effects on both humoral and cellular immune responses.5-9 Data also indicate that carprofen inhibits the production ...



