7T Gummy ES Chewable Tablets
Generic name:acetaminophen
Dosage form: tablet, chewable
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 23, 2021.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
7TGummy ES(Acetaminophen Chewable Gels 500 mg)
7T Pharma, LLC
----------------
On This Page
7T Gummy ES Chewable Tablets Description
7T Gummy ES is available as a chewable gel or gummy oral dosage form with improved organoleptic properties of taste, softness, chewiness, hardness, and translucency.
Acetaminophen, 4’-hydroxyacetanilide, a slightly bitter, white, odorless, crystalline powder, is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. It has the following structural formula:
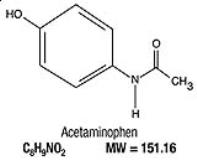
In addition, each chewable gel contains the following inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl betadex, seaweed extract (carrageenan), maltitol solution, sugar, sodium citrate, sodium chloride, sucralose, neotame, maltodextrin, glucose syrup, flavor, purified water.
7T Gummy ES Chewable Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism or Action
The precise mechanism of the analgesic properties of acetaminophen is not established but is thought to involve central nervous system actions.
Pharmacodynamics
Therapeutic doses of acetaminophen have negligible effects on the cardiovascular or respiratory systems; however, toxic doses may cause circulatory failure and rapid, shallow breathing.
Pharmacokinetics
Acetaminophen is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed throughout most body tissues. A small fraction (10 to 25%) of acetaminophen is bound to plasma proteins. The plasma half-life is 1.25 to 3 hours, but may be increased by liver damage and following overdosage. Elimination of acetaminophen is principally by liver metabolism (conjugation) and subsequent renal excretion of metabolites. Acetaminophen is primarily metabolized in the liver by first-order kinetics and involves three principal separate pathways: conjugation with glucuronide; conjugation with sulfate; and oxidation via the cytochrome, P450-dependent, mixed-function oxidase enzyme pathway to form a reactive intermediate metabolite, which conjugates with glutathione a..



