Bretylium Injection
Generic name: bretylium tosylate
Dosage form: injection
Drug class:Group III antiarrhythmics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 1, 2020.
On This Page
Rx only
AQUEOUS SOLUTION FOR THE ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS
Glass Vial
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR OR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
DESCRIPTION
Bretylium Tosylate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for use in the management of ventricular arrhythmias.
Each milliliter contains 50 mg bretylium tosylate in water for injection. The osmolarity is 0.174 mOsm/mL (approx.). May contain sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment. pH is approximately 5.2.
The solution contains no bacteriostatic, antimicrobial agent or added buffer (except for pH adjustment) and is intended only for use as a single-dose administration. When smaller doses are required, the unused portion should be discarded.
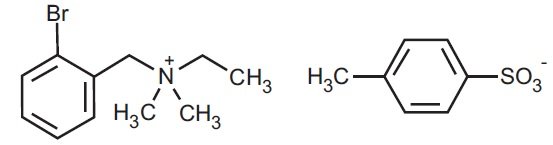
Bretylium tosylate, a bromobenzyl quaternary ammonium compound is chemically designated (o-Bromobenzyl) ethyldimethyl-ammonium p-toluenesulfonate, a white powder freely soluble in water. It has the following structural formula:
Therapeutic class: Bretylium tosylate is classified as an antiarrhythmic agent.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Bretylium tosylate selectively accumulates in sympathetic ganglia and their postganglionic adrenergic neurons when administered slowly or incrementally where it inhibits norepinephrine release by depressing adrenergic nerve terminal excitability.
Bretylium tosylate also suppresses ventricular fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmias. The mechanisms of the antifibrillatory and antiarrhythmic actions of bretylium tosylate are not established.
In efforts to define these mechanisms, the following electrophysiologic actions of bretylium tosylate have been demonstrated in animal experiments:
- 1.
- Increase in ventricular fibrillation threshold.
- 2.
- Increase in action potential duration and effective refractory period without changes in heart rate.
- 3.
- Little effect on the rate of rise or amplitude of the cardiac action potential (Phase 0) or in resting membrane potential (Phase 4) in normal myocardium. However, when cell injury slows the rate of rise, decreases amplitude, and lowers resting memb...