Carnitor Injection
Generic name:levocarnitine
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class:Nutraceutical products
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 1, 2021.
On This Page
Carnitor Injection Description
CARNITOR ® (levocarnitine) is a carrier molecule in the transport of long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
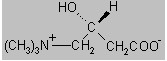
The chemical name of levocarnitine is 3-carboxy-2( R)-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium, inner salt. Levocarnitine is a white crystalline, hygroscopic powder. It is readily soluble in water, hot alcohol, and insoluble in acetone. The specific rotation of levocarnitine is between -29° and -32°. Its chemical structure is:
Empirical Formula: C 7H 15NO 3
Molecular Weight: 161.20
CARNITOR ® (levocarnitine) Injection is a sterile aqueous solution containing 1 g of levocarnitine per 5 mL vial. The pH is adjusted to 6.0 - 6.5 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Carnitor Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
CARNITOR ® (levocarnitine) is a naturally occurring substance required in mammalian energy metabolism. It has been shown to facilitate long-chain fatty acid entry into cellular mitochondria, thereby delivering substrate for oxidation and subsequent energy production. Fatty acids are utilized as an energy substrate in all tissues except the brain. In skeletal and cardiac muscle, fatty acids are the main substrate for energy production.
Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is characterized by low concentrations of levocarnitine in plasma, RBC, and/or tissues. It has not been possible to determine which symptoms are due to carnitine deficiency and which are due to an underlying organic acidemia, as symptoms of both abnormalities may be expected to improve with CARNITOR ®. The literature reports that carnitine can promote the excretion of excess organic or fatty acids in patients with defects in fatty acid metabolism and/or specific organic acidopathies that bioaccumulate acylCoA es...