Duocaine
Generic name: lidocaine hydrochloride and bupivacaine hydrochloride
Dosage form: injection
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 22, 2021.
On This Page
Duocaine Description
Duocaine™ is a sterile aqueous solution that contains a mixture of local anesthetic agents, 1% lidocaine and 0.375% bupivacaine.
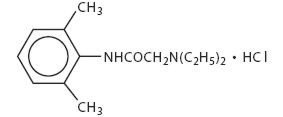
Duocaine™ solution contains lidocaine HCl, which is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2, 6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride and has a molecular weight of 270.80. Lidocaine HCl (C14H22N2O•HCl) has the following structure:
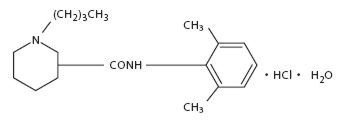
Duocaine™ solution also contains bupivacaine HCl, which is chemically designated as 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate, a white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in 95 percent ethanol, soluble in water, and slightly soluble in chloroform or acetone and has a molecular weight of 342.90. Bupivacaine HCl (C18H28N2O•HCl•H2O) has the following structure:
Bupivacaine and lidocaine are related chemically and pharmacologically to the aminoacyl local anesthetics. Bupivacaine is a homologue of mepivacaine, and all three of these anesthetics contain an amide linkage between the aromatic nucleus and the amino or piperidine group. They differ in this respect from the procaine-type local anesthetics, which have an ester linkage.
The pKa of bupivacaine (8.1) is similar to that of lidocaine (7.86). However, bupivacaine possesses a greater degree of lipid solubility and is protein bound to a greater extent than lidocaine.
Each mL of Duocaine contains: Actives: lidocaine HCl 10 mg, bupivaoaine HCl 3.75 mg. Inactives: sodium chloride, purified water, and hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH. It has an osmolality of 280 to 350 mOsmol/kg and a pH of 5.0 to 6.5.
Duocaine - Clinical Pharmacology
Duocaine™ blocks the generation and conduction of nerve impulses, presumably increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by r...



