Erythrocin
Generic name:erythromycin stearate
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug class:Macrolides
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 22, 2021.
On This Page
Film-coated Tablets
Rx only
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Erythrocin® STEARATE Film-coated tablets and other antibacterial drugs, Erythrocin® STEARATE Film-coated tablets should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
Erythrocin Description
Erythrocin® STEARATE Film-coated tablets (erythromycin stearate tablets, USP) are an antibacterial product containing the stearate salt of erythromycin in a unique film coating.
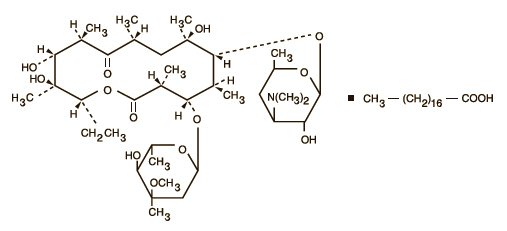
Erythromycin is produced by a strain of Saccharopolyspora erythraea (formerly Streptomyces erythraeus) and belongs to the macrolide group of antibiotics. It is basic and readily forms salts with acids. Erythromycin is a white to off-white powder, slightly soluble in water, and soluble in alcohol, chloroform, and ether. Erythromycin stearate is known chemically as erythromycin octadecanoate. The molecular formula of erythromycin stearate is C37H67NO13 ∙ C18H36O2, and the molecular weight is 1018.43. The structural formula is:
Inactive Ingredients
250 mg tablet: Cellulosic polymers, corn starch, D&C Red No. 7, polacrilin potassium, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, sodium citrate, sorbic acid, sorbitan monooleate and titanium dioxide.
Erythrocin - Clinical Pharmacology
Orally administered erythromycin base and its salts are readily absorbed in the microbiologically active form. Interindividual variations in the absorption of erythromycin are, however, observed, and some patients do not achieve optimal serum levels. Erythromycin is largely bound to plasma ...



