FerraPlus 90
Generic name: docusate sodium, folic acid, iron, cyanocobalamin, and ascorbic acid
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Drug classes:Iron products, Vitamin and mineral combinations
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 1, 2022.
On This Page
SUPPLEMENT FACTS
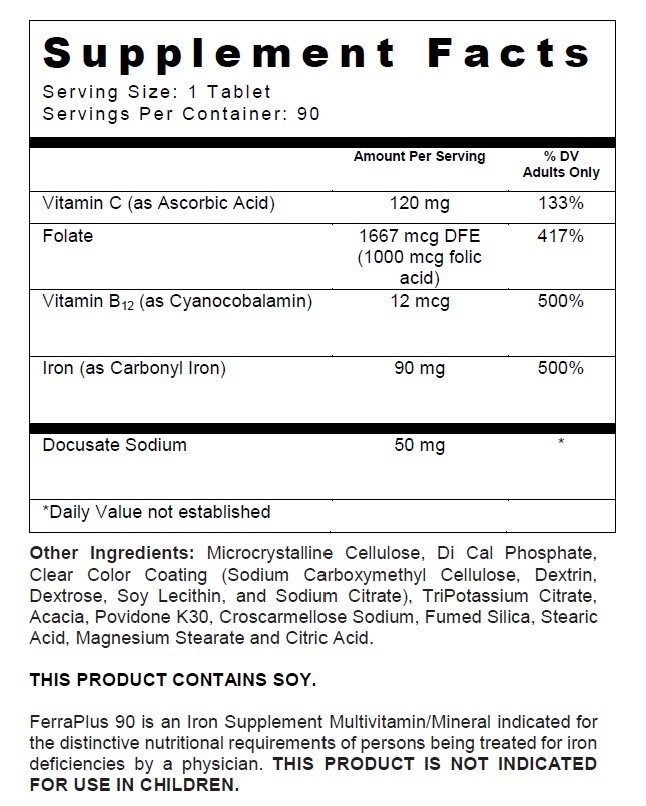
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients. Hemolytic anemia, hemochromatosis, and hemosiderosis are contraindications to iron therapy.
Warnings
Folic acid alone is improper therapy in the treatment of pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias where vitamin B12 is deficient.

Precautions
General: Take 2 hours after meals. Do not exceed recommended dose. Discontinue use if symptoms of intolerance appear. The type of anemia and underlying cause or causes should be determined before starting therapy with FerraPlus 90 tablets. Ensure Hgb, Hct, reticulocyte count are determined before starting therapy and periodically thereafter during prolonged treatment. Periodically review therapy to determine if it needs to be continued without change or if a dose change or if a dose change is indicated.
Folic Acid: Folic acid in doses above 0.1 mg daily may obscure pernicious anemia assessment, such that hematologic remission can occur while neurological manifestations remain progressive. Pernicious anemia should be excluded before using these products since folic acid may mask the symptoms of pernicious anemia.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of this product have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of this product have not been established in elderly patients.
Drug Interactions
Prescriber should be aware of a number of iron/drug interactions, including antacids, tetracyclines, or fluoroquinolones.
Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions with iron therapy may include GI irritation, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and dark stools. Adverse reactions with iron therapy are usually transient. Allergic sensitization has been reported following both oral and parenteral administration of folic acid.
Overdosage
Symptoms: Abdominal pain, metabolic acidosis, anuria, CNS damage, coma, convulsions, death, dehydration, diffuse vascular congestion, hepatic cirrhosis, hypotension, hypothermia, l...



