Melphalan Tablets
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class:Alkylating agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 1, 2021.
On This Page
Melphalan Tablets USP should be administered under the supervision of a qualified physician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Severe bone marrow suppression with resulting infection or bleeding may occur. Melphalan is leukemogenic in humans.
Melphalan produces chromosomal aberrations in vitro and in vivo and, therefore, should be considered potentially mutagenic in humans.
Melphalan Tablets Description
Melphalan, also known as L-phenylalanine mustard, phenylalanine mustard, L-PAM, or L-sarcolysin, is a phenylalanine derivative of nitrogen mustard. Melphalan is a bifunctional alkylating agent which is active against selective human neoplastic diseases. It is known chemically as 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine. The molecular formula is C13H18Cl2N2O2 and the molecular weight is 305.20. The structural formula is:
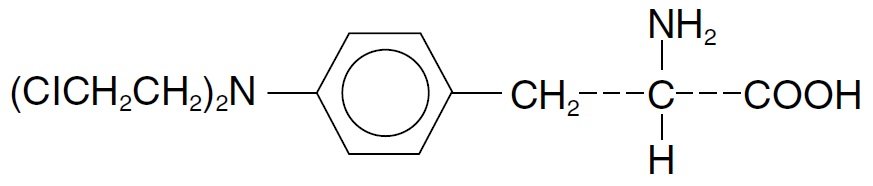
Melphalan is the active L-isomer of the compound and was first synthesized in 1953 by Bergel and Stock; the D-isomer, known as medphalan, is less active against certain animal tumors, and the dose needed to produce effects on chromosomes is larger than that required with the L-isomer. The racemic (DL–) form is known as merphalan or sarcolysin.
Melphalan is practically insoluble in water and has a pKa1 of ∼2.5.
Melphalan is available in tablet form for oral administration. Each film-coated tablet contains 2 mg melphalan USP and the inactive ingredients microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and polyethylene glycol.
Melphalan Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
Melphalan is an alkylating agent of the bischloroethylamine type. As a result, its cytotoxicity appears to be related to the extent of its int...



